When HMS Sirius was wrecked off Norfolk Island in 1790, the loss was keenly felt back in Sydney. She was one of only two ships available to Governor Phillip, and he desperately needed both of them. Sydney had so far been unable to grow sufficient food to feed itself and was now facing starvation. The loss of the Sirius only compounded the colony’s problems.
HMS Sirius had sailed from Portsmouth on 13 March 1787 as part of the First Fleet, a social experiment to rid England of its most troublesome and unwanted folk. They arrived in New South Wales in January 1788. A month later HMS Supply sailed for Norfolk Island with a small number of convicts and a detachment of guards to establish a penal settlement there. By October of the same year, Governor Phillip realised that Sydney would soon be facing starvation unless something was urgently done. He ordered Captain John Hunter to sail HMS Sirius to the Cape of Good Hope and purchase livestock, grain and other provisions for the fledgling colony.
Some months after her return, the Sirius, in company with HMS Supply, was ordered to sail for Norfolk Island with desperately needed provisions along with additional convicts and guards.

They reached Norfolk Island on 13 March 1790, and over the next few days, they disembarked their passengers; however, the sea conditions were such that neither ship was able to land its stores. On 15 March, the unrelenting gale-force southerly forced them to leave the island. By the 19th, the wind had moderated and shifted around to the southeast, so Captain Hunter made landfall again, hoping to begin unloading.
As Sirius neared the island, Captain Hunter saw the Supply already anchored in Sydney Bay, and there were signals flying on shore that longboats could land without danger from the surf. Hunter took his ship in as close as he dared, loaded the boats and sent them away, but then the wind freshened.

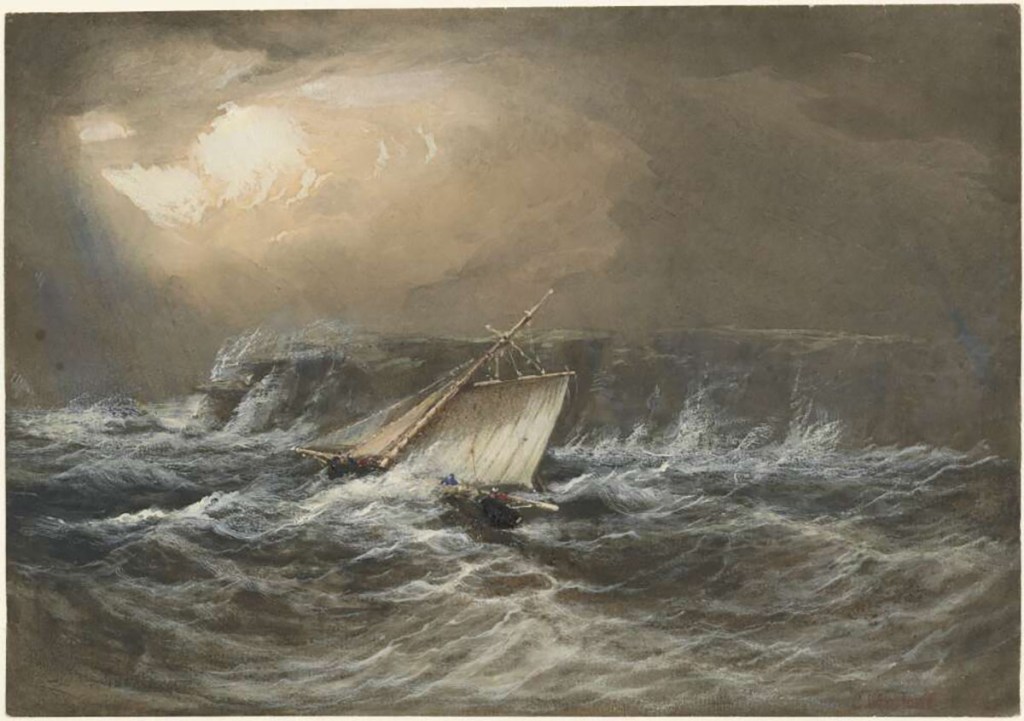
Hunter ordered his men to haul up the anchor and make for open water, but before he could do so, the Sirius was driven onto the rocks. Powerful surf crashed around the stricken ship. Soon after they struck, the carpenter reported that water was pouring into the hold. The masts were cut away in the hope that the lightened vessel might be driven higher onto the reef, where the crew would have a better chance of saving their lives.
By now, it was about 11 a.m. The provisions were brought up from the hold and stacked on deck so they might be floated ashore if the opportunity arose. However, the sea conditions continued to deteriorate. Towards evening, Hunter received word from shore urging him to abandon ship as it would be too dangerous to remain overnight. A rope was tied to an empty barrel and floated through the surf to waiting hands ashore. Then a seven-inch-thick hawser was sent across the narrow stretch of reef and surging seas and tied to a tree. Now the crew could be hauled ashore three or four at a time. Most sported cuts or bruises by the time the reached land from being bashed against the rocks on the perilous passage. The operation stopped only when it became too dark to continue safely, and the remaining men were taken off the following day.
A couple of days later, two convicts volunteered to go aboard the Sirius to get the livestock ashore. They got a number of pigs and some poultry over the side and the current did the rest. However, as evening turned to night, the two convicts refused to leave the ship. They had found a cask of rum sometime during the day, and by evening, they were drunk as lords. Probably in an effort to keep themselves warm, they lit two fires, but they soon got out of hand and did significant damage to the ship. The following day, guards were sent out to the ship to forcibly return them to shore, where they were clapped in irons for their troubles.
When the weather finally eased, Hunter sent some of his men across to begin ferrying the remaining provisions ashore using the hawser. Other stores, sealed in timber casks, were thrown into the water with the hope that they would wash ashore through the surf. Some made it. Some sank to the bottom.
While the Supply had managed to unload its provisions on the sheltered side of the island, with so many additional mouths to feed, rations for everyone on Norfolk were cut in half.

Captain Hunter and his crew would be stranded on Norfolk Island for several months before they could return to Sydney. Meanwhile, Governor Phillip was stunned to learn of the Sirius’ loss. He had been relying on her to go on another resupply mission to keep the struggling colony fed.
His problems just kept mounting. The second fleet had recently arrived, delivering 800 extra mouths to feed, many were already in a terrible physical state when they came ashore. They were too ill to help cultivate crops or contribute in any other meaningful way. One of the fleet’s two supply ships, HMS Guardian, had been wrecked in the Southern Ocean, placing a greater strain on the settlement’s already meagre provisions. Food was tightly rationed and no distinction was made between the lowest convict and the Governor himself. Everyone received the same ration, one and a half pounds (700 g) of flour, two pounds (900 g) of salt pork, one pound (450 g) of rice and one pint (500ml) of peas per week.
The few privately owned boats in Sydney were requisitioned and sent out to catch fish. Hunting parties roamed the outskirts in search of game, and guards had to be stationed around the public vegetable gardens to prevent theft. HMS Supply was sent to Batavia for supplies, leaving Sydney without a single ship at its disposal. One hundred forty-three people died of sickness or malnutrition in Sydney that year. There was probably no other time when the existence of the settlement looked so tenuous.

© Copyright C.J. Ison / Tales from the Quarterdeck, 2023.
To be notified of future blogs, please enter your email address below.