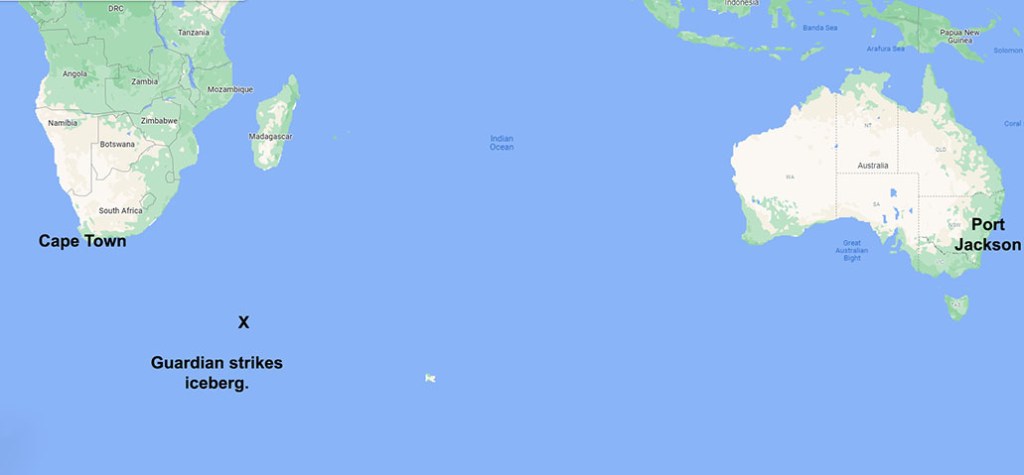
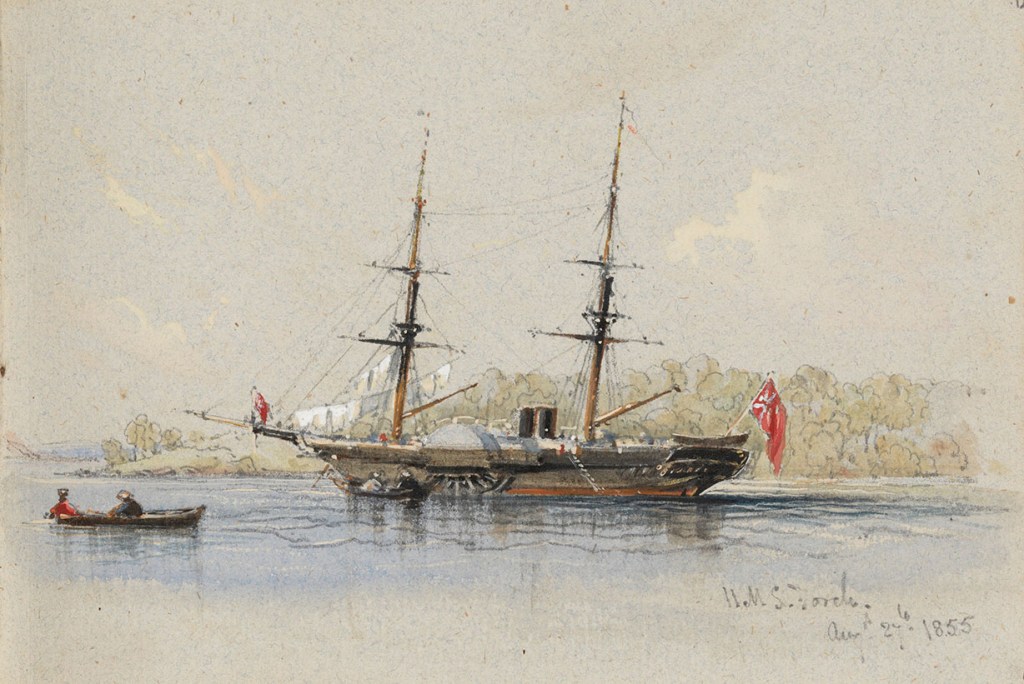In February 1872, the crew of HMS Basilisk found 14 men barely clinging to life on a derelict schooner adrift off the far north Queensland coast. The vessel’s name was not immediately apparent, and none of the survivors spoke English. It was a mystery as to how the ship came to be in those remote northern waters, and one that would take some time to solve.
The side paddle steamer HMS Basilisk was steaming up the Queensland coast on a three-month cruise around Torres Strait. They were to deliver stores to the government settlement at Somerset, chart several recently reported navigation hazards and generally show the flag in that remote part of the continent.
When the Basilisk was in the vicinity of Hinchinbrook Island, a lookout sighted a small fore-and-aft schooner off in the distance. It was rare to come upon another ship in those waters, so Captain John Moresby called for his telescope and examined the ship more closely. It was immediately clear to the master mariner that not all was as it should be with the strange vessel.
Moresby noticed that the schooner sat heavily in the water as she sluggishly rode the long, smooth swells. His first thought was that her crew must have abandoned her for some reason. As the Basilisk drew closer, Moresby could see that her weather-beaten sails were poorly set and flapping loosely in the light breeze. The rigging was slack, and there was no sign of anyone on deck.

When the Basilisk raised her ensign, signalling to the strange vessel to identify itself, they got no response. But as they drew nearer still, a couple of Pacific Islanders armed with muskets staggered to their feet near the schooner’s stern. Moresby then spotted several more men lying scattered on the deck. He sent two boats across to investigate.
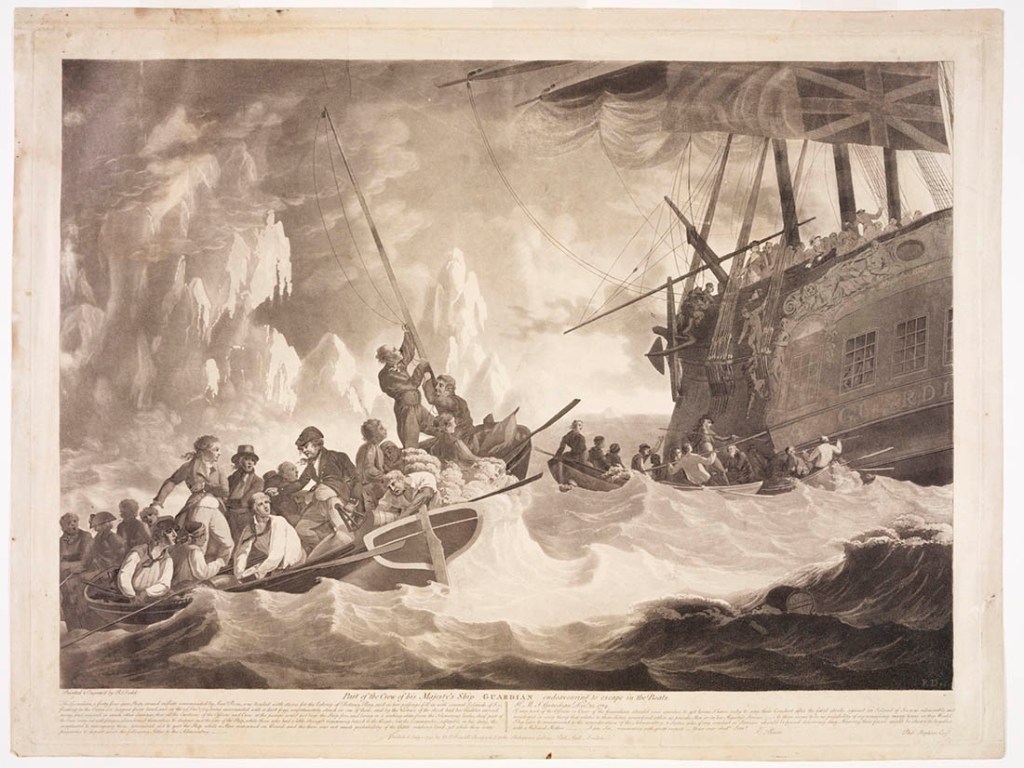
What the sailors found is best summed up in Captain Moresby’s own words: “… they were living skeletons, creatures dazed with fear and mortal weakness. As our crews boarded, other half-dead wretches tottered to their feet, fumbling too at rusty, lockless muskets. … They were dreadful to look at – being in the last stage of famine, wasted to the bone; some were barely alive, and the sleeping figures were dead bodies fast losing the shape of humanity, on a deck foul with blood.”
The boarding party found several dead and decomposing bodies on the deck. There was five feet of putrid water sloshing about in the hold. The cabin had been ransacked, and the deck bore the marks of numerous axe strokes. Parts of the deck were also stained brown by large pools of what appeared to be dried blood. And, there was no fresh water or food anywhere to be found. All the evidence, Captain Moresby later recalled, pointed to a violent and tragic incident having taken place on board the schooner. Moresby held a funeral service for the dead and buried them at sea. He then steamed towards Cardwell, 40 km away with the schooner in tow. He landed the 14 survivors, none of whom spoke any English, but for the word “Solomon.” Moresby assumed they meant they were from the Solomon Islands. He then continued North towards Torres Strait, leaving Midshipman Sabben in charge of several sailors and the schooner. He would collect them in a couple of months on his return to Sydney.

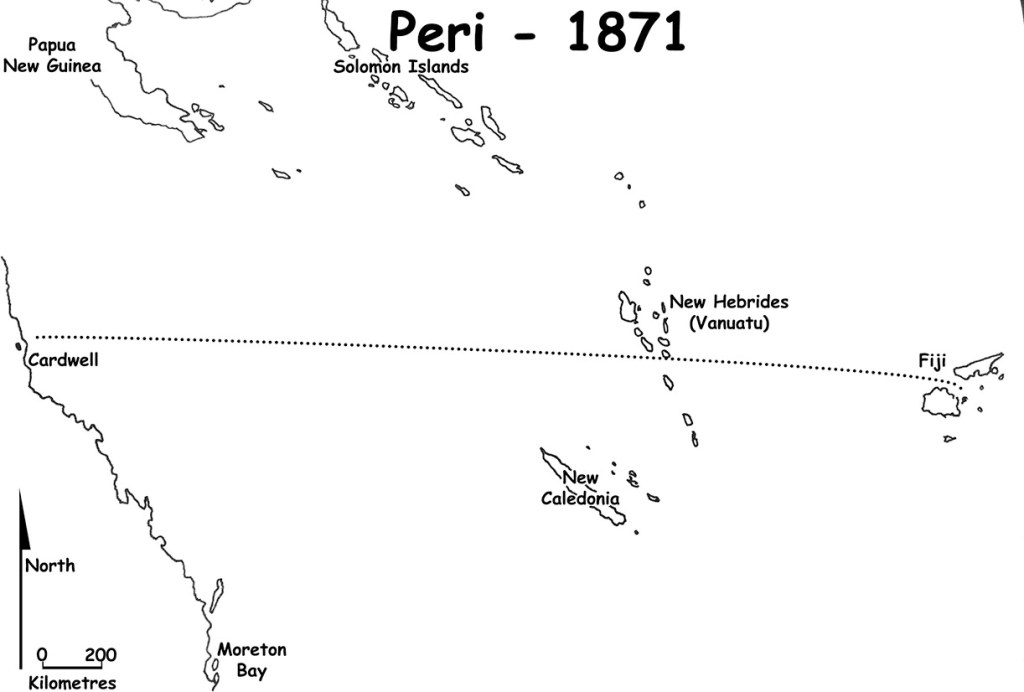
The pieces of the puzzle would slowly come together over the next weeks and months. After Sabben’s men had scrubbed the headboards clean, they discovered the schooner was called the Peri. The Peri had recently been reported missing in Fijian waters. On 27 December 1871, she had sailed from Viti Levu with approximately 90 “indentured” Pacific Islanders bound for a cotton plantation on Taveuni, 100 km away, but she never arrived.
About 30 of those 90 men had been kidnapped in the Solomon Islands and taken to Levuka in Fiji. At the time, the South Pacific was in the midst of a cotton boom, and the white plantation owners struggled to find enough field workers or kanakas to tend their crops. Many Islanders fell victim to more unscrupulous “recruiters” who stopped at nothing to fill their quotas.
At Levuka, kanakas were disembarked and sold to plantation owners to serve three-year contracts. At the completion of their time, it was the plantation owners’ responsibility to pay off their workers and return them to their home islands. The kanakas themselves were supposed to have willingly agreed to the arrangements and be appropriately compensated for their labour; however, that was not always the case.
In this instance, the kidnapped Solomon Islanders were sent to an Australian plantation owner on Taveuni Island. But while in transit, they seized control of the cutter and escaped. The vessel was later found aground on a small island in the Yasawa group, and most of the men were recaptured a couple of weeks later.
The other 60 or so Islanders who had been on the Peri had likely also been recently kidnapped. They had fallen into the clutches of a notorious blackbirder named Captain McLever. By December 1871, both groups of kidnapped men had been transferred to the Peri and were about to be sent to work on a plantation on Taveuni Island.
It is not entirely clear what happened next, but it seems the 90 kanakas rebelled, killed the captain and crew and seized the ship. Over the next six weeks, they sailed or drifted nearly 3500 km west until they were found by the Basilisk off the Australian coast. From the water in the hold and the general state of the ship, Moresby believed they had weathered at least one severe tropical storm during their passage. And judging by their emaciated state, food and water had run out long before they were rescued. The blood stains and axe marks led some to speculate that the survivors may have resorted to cannibalism, but that was never conclusively proved, and none of the bodies found showed signs of having been butchered.
By the time the Basilisk‘s crew boarded the schooner, there were just 14 men still alive. One more would succumb soon after being put ashore at Cardwell.
The remaining 13 Solomon Islanders were taken to Sydney by the Basilisk on her return from Torres Strait and eventually sent back to Fiji on HMS Cossack so they might be repatriated. However, eight jumped ship when the Cossack stopped briefly at Matuku Island, perhaps fearing they were being returned to Fiji to be punished. When the last five Peri survivors were finally questioned through an interpreter in Levuka, they told the British Consul that they had been kidnapped. They described how, when they paddled out to Captain McLever’s ship, their canoes were sunk and they had been beaten and locked in the hold.
McLever was arrested, and the Solomon Islanders were taken back to Sydney so they could testify at his trial. However, no one had thought to send a translator, and the case was dismissed for lack of evidence. The Islanders were sent back to Fiji, but what happened to them after that is unknown.

1.Moresby. John RN, Discoveries and Surveys in New Guinea and D’Entrecasteaux Islands, John Murray, London, 1876, p.4.
© Copyright C.J. Ison / Tales from the Quarterdeck, 2022.
To be notified of future blogs, please enter your email address below.