Sixty bite-sized stories from Australia’s maritime past

I have just launched a new book titled Tales from the Quarterdeck: Sixty bite-sized stories from Australia’s maritime past. Sixty of the most popular posts have been reedited. In some cases, I’ve rewritten a couple and updated a few where new information has come to light since first writing them.
For those who would value ready access to the stories in their bookcase, Tales from the Quarterdeck is available in Kindle ebook and paperback formats through Amazon.
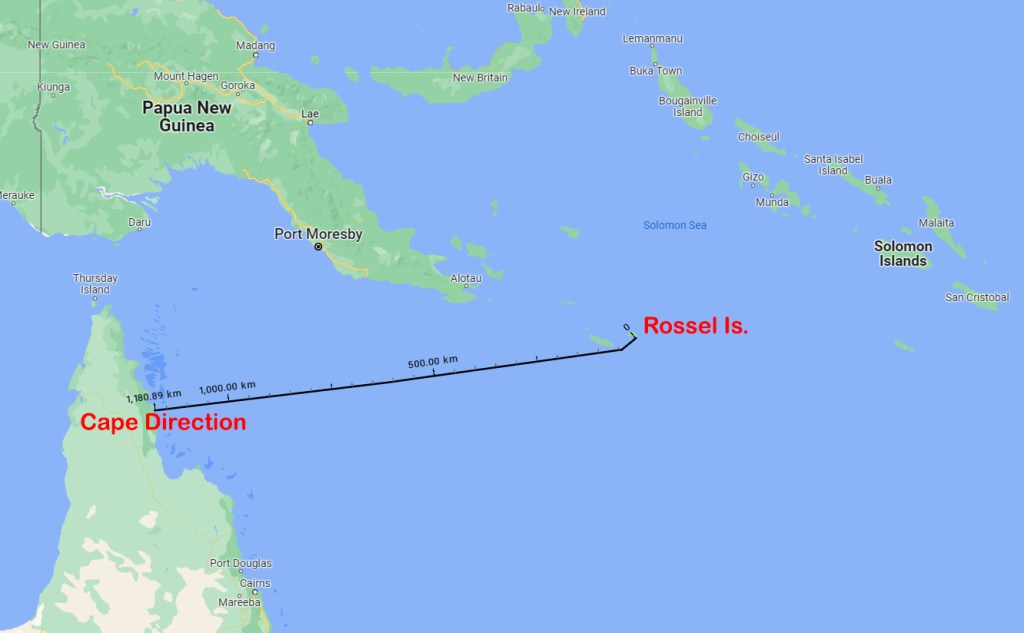
The stories are organised in chronological order, starting with the Tryall shipwreck off the Western Australian coast in 1622, and finishing with the Second World War exploits of the Krait. See below for a full list of the stories covered in the book.

1622 – The Tryall: Australia’s earliest shipwreck
1629 – The Batavia Tragedy
1688 – William Dampier: Navigator, naturalist, writer, pirate
1770 – The Endeavour’s Crappy Repair
1788 – Loss of La Astrolabe and La Boussole, a 40-Year Mystery
1789 – Bligh’s Epic Voyage to Timor
1789 – HMS Guardian: All Hands to the Pumps
1790 – The Loss of HMS Sirius
1790 – Sydney’s First Desperate Escape
1791 – HMS Pandora: Queensland’s earliest recorded Shipwreck
1791 – William Bryant’s Great Escape
1797 – The Loss of the Sydney Cove
1803 – Loss of HMS Porpoise
1808 – Robert Stewart and the Seizure of the Harrington
1814 – Wreck of the Morning Star
1816 – The Life and Loss of HMSC Mermaid
1824 – The Brig Amity’s Amazing Career
1829 – The Cyprus mutiny
1831 – The Caledonia’s perilous last voyage
1833 – The Badger’s Textbook Escape
1835 – The Loss of the Convict Ship Neva
1835 – The Post Office in the middle of nowhere
1835 – The Tragic Loss of George III
1845 – The Cataraqui: Australia’s worst shipwreck
1846 – The Peruvian’s Lone Survivor
1847 – The Foundering of the Sovereign
1850 – The Loss of the Enchantress: A first-hand account
1851 – The Countess of Minto’s brush with Disaster
1852 – The Bourneuf’s Tragic Last Voyage
1852 – The Nelson Gold Heist

1854 – Bato to the Rescue
1854 – HMS Torch and the rescue of the Ningpo
1856 – The Loss of the Duroc and the Rise of La Deliverance
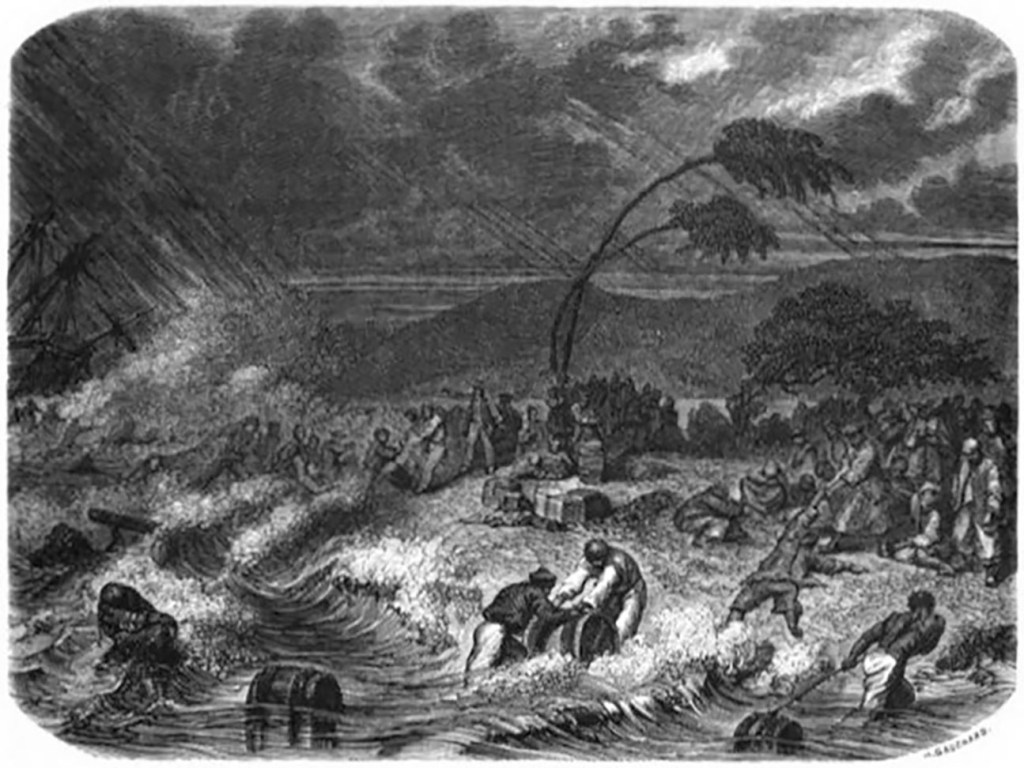
1858 – The Loss of the Saint Paul and its Horrific Aftermath
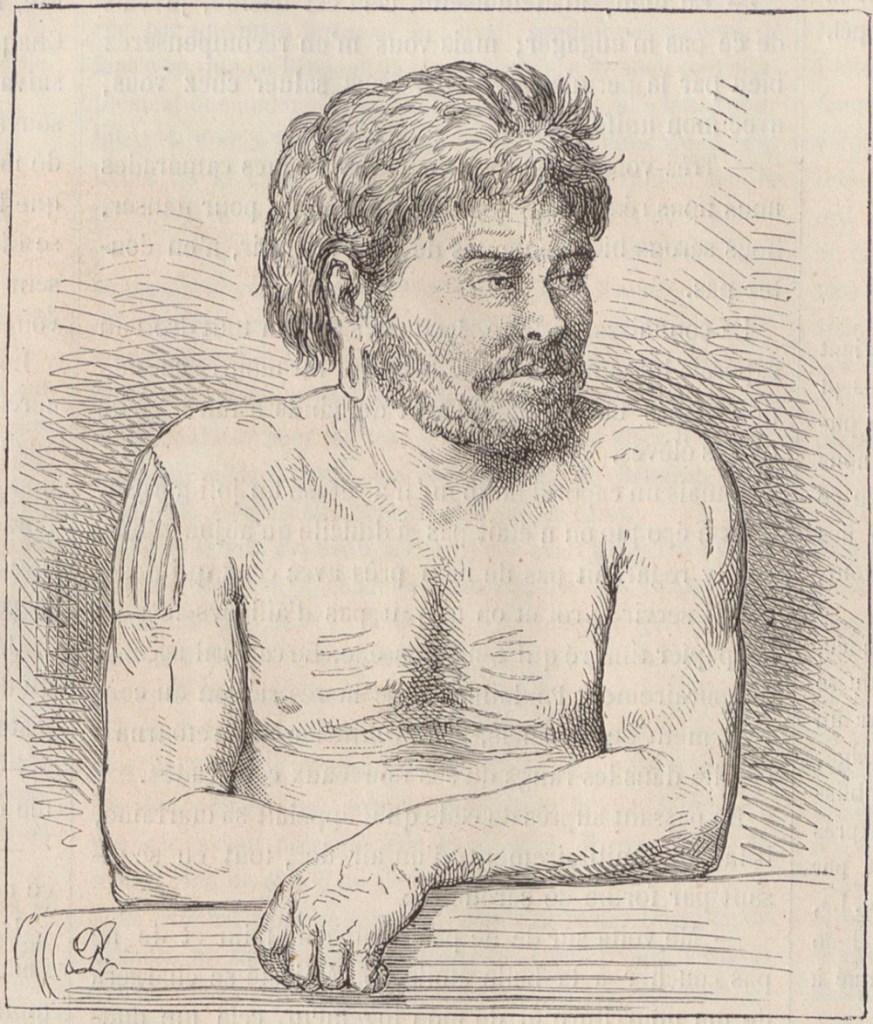
1858 – Narcisse Pelletier, An Extraordinary Tale of Survival
1859 – The Indian Queen’s Icy Encounter
1859 – The Sapphire and Marina
1863 – The loss of the Grafton: Marooned for twenty months
1864 – The Invercauld shipwreck
1865 – The CSS Shenandoah: Victoria’s link to the American Civil War
1866 – The Loss of the SS Cawarra: Bad luck or an avoidable tragedy?
1868 – The Bogus Count and Hamlet’s Ghost
1871 – The Mystery of the Peri
1872 – The Loss of the Maria, A Cautionary Tale
1875 – The Tragedy behind the Gothenburg Medals
1876 – The Catalpa rescue
1876 – The Banshee’s Terrible Loss
1878 – The Loch Ard Tragedy
1884 – The Macabre case of the Mignonette
1885 – The Douro and its Piratical Captain
1889 – The Windjammer Grace Harwar
1891 – The Spanish Silver of Torres Strait
1893 – The Foundering of the SS Alert
1895 – The Norna and the Conman Commodore
1899 – Cyclone Mahina
1911 – The Loss of the Mandalay
1918 – The Orete’s Robinson Crusoe-like Castaway
1935 – The Life and Loss of the SS Maheno
1943 – Surviving the Centaur Sinking
1943 – The Amazing Krait