
Sometime around 1891, a group of beche-de-mer fishermen stumbled upon a huge hoard of Spanish silver coins. The men had been fishing in the shallow waters of the Eastern Fields at the eastern approach to Torres Strait when they made the surprise discovery.
At low tide, when much of the reef was exposed, they spotted an old, coral-encrusted anchor fluke jutting from the reef’s surface. The shoals of Torres Strait had claimed many a ship during the 19th Century, and the fishermen were keen to see what else they might find.
They began chipping away at the decades of accumulated growth until the anchor finally broke free from the surrounding coral. When it was rolled clear, a mass of silver coins, all fused together by time and saltwater, was revealed. Buoyed by the find, the fishermen forgot about the beche-de-mer and extended their excavations. Each day, as soon as the falling tide exposed the reef, they got to work chipping away at the coral. In the end, they uncovered a staggering 410 kgs (900 pounds) of silver. It took them two trips to carry it all back to Somerset, the fishing and cattle station near the tip of Cape York owned by the early pioneering family of Frank Jardine.

At the time, it was supposed that the coins might have been carried on a Spanish ship on her way to Manila to pay the wages of the civil and military staff. Either that, or it was to be used to purchase spices from traders in the Indonesian Archipelago, further to the west. Regardless, the ship that had been carrying the fortune in silver had ended its voyage on that remote coral outcrop many decades earlier. They knew it was an old wreck, for by 1891, the timbers had long since rotted away.
The mystery was only solved years later. It turned out not to have been a Spanish galleon at all. Instead, the fishermen had stumbled upon the remains of the English brig, Sun, which had been lost in Torres Strait in May 1826. Earlier that same year, the Sun had delivered a cargo of tea from China to merchants in Hobart and Sydney. In Sydney, a local businessman had entrusted the ship and her captain with a new cargo of between 30,000 and 40,000 Spanish silver dollars. At the time, one Spanish dollar was worth 4 shillings and 4 pence, which would have valued the somewhere between £7,000 and £10,000. In today’s money, the silver content alone would be worth well over one million Australian dollars.
The Sun sailed from Sydney on 7 May, bound for Singapore by way of Torres Strait. But it never arrived. The voyage was cut short three weeks later when the Sun struck a submerged reef as it attempted to navigate the dangerous waters separating Cape York from New Guinea.
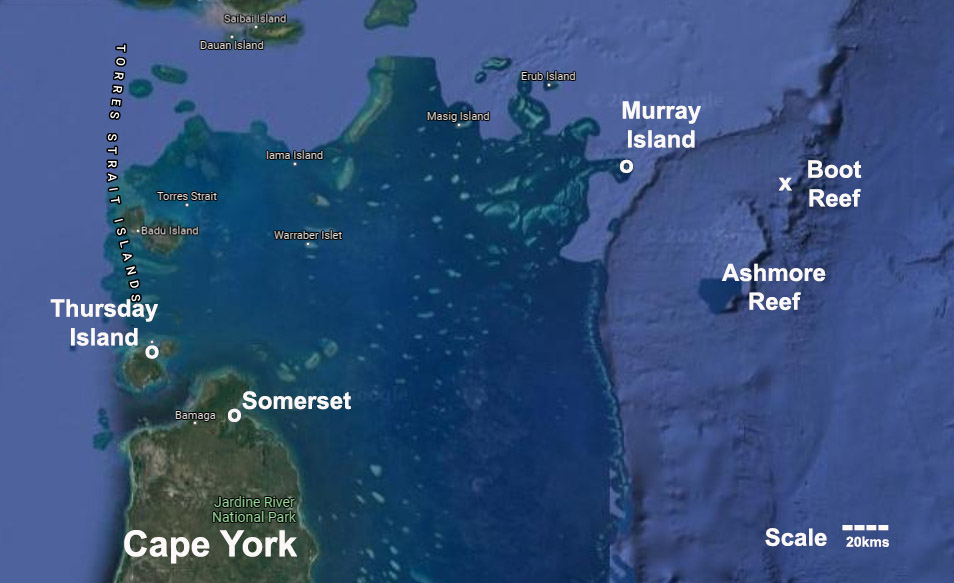
The ship broke up almost immediately. Captain Gillet and his crew took to the longboat and jolly boat and made for Murray Island, about 30 nm (60 km) away. Such was the haste with which they were forced to abandon the ship that there was certainly no time to save the silver. The crew didn’t even have time to provision the boats with food or water before they pushed away from the wreck. Fortunately, they would only be at sea for two days before sighting land.
As fate would have it, just as their safety seemed assured, the longboat struck a reef and capsized, spilling all the occupants into the water. The first and second mates, plus 22 lascar sailors, drowned. Only the jolly boat with the ship’s captain and 11 remaining seamen reached Murray Island, where they were looked after by the Islanders. Three days later, Captain Gillet and his men were rescued by a passing ship and eventually delivered to Calcutta, where he reported the loss of his ship.
So, there the Spanish silver dollars remained undisturbed for the next 65 years as the Sun slowly disintegrated around them. As the employer of the fishermen, Frank Jardine claimed the lion’s share of the haul. He reportedly had at least some of the coins melted down and made into silver tableware and cutlery for the Jardine Homestead.

© Copyright C.J. Ison, Tales from the Quarterdeck, 2021.
Enter your email address below to be notified of new posts.


