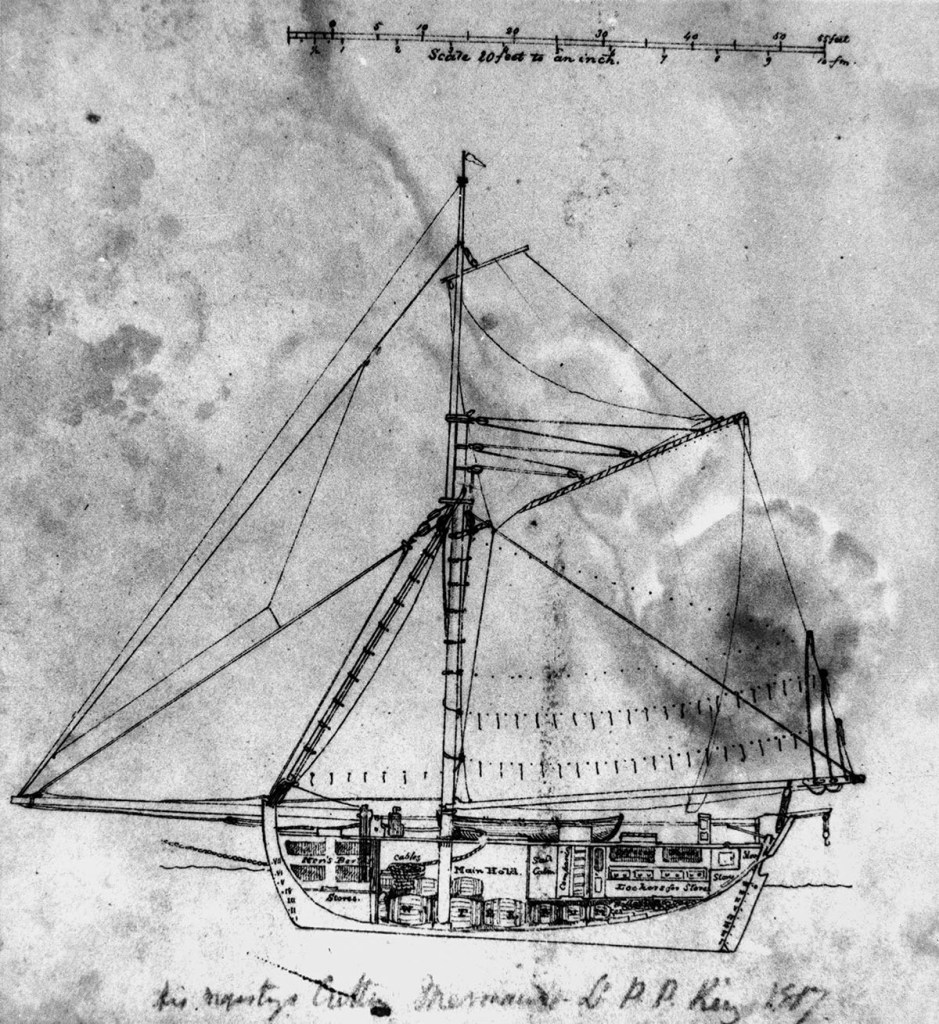
Between 1818 and 1820, the small survey cutter HMSC Mermaid played an important role in charting Australia’s vast coastline. So, it is perhaps ironic that her last voyage should have been cut short on an uncharted reef off the north Queensland coast.
The Mermaid was an 84-ton cutter launched in Calcutta in 1816. She arrived in New South Wales the following year and was soon purchased by the Government to undertake survey work requested by the British Admiralty.
Lieutenant Phillip Parker King was dispatched to Australia to carry out a detailed survey of the Australian coastline, particularly those areas bypassed by Matthew Flinders. The son of former NSW Governor Phillip Gidley King, he had been born on Norfolk Island in 1791. On the family’s return to England and completion of his schooling, the young King joined the Royal Navy. He was given command of the Mermaid and got to work.

HMSC Mermaid made three extensive voyages under King. They sailed from Sydney on 22 Dec 1817, bound for Australia’s northern and northwest coasts via Bass Strait and Cape Leeuwin. The crew included two sailing masters, 12 seamen and two boys. On board were also the botanist Allan Cunningham and Bungaree, a Kuring-gai man from Broken Bay who had also circumnavigated the continent with Matthew Flinders on the Investigator.
At Northwest Cape, King surveyed and named Exmouth Gulf before continuing north along the coast until they reached Van Diemen’s Gulf and Cobourg Peninsula. From there, they sailed to Kupang on Timor Island to resupply, where they remained for two weeks. King then set sail for Sydney, returning down the West Australian coast. The return trip was marred by rough weather and a shortage of manpower. Several of the crew had become seriously ill shortly after leaving Timor, and one of them subsequently died. Despite the hardships, the Mermaid arrived back in Sydney on 29 July 1818 after an absence of seven months and seven days.
Between December 1818 and January 1819, King sailed to Van Diemen’s Land and undertook a survey of Macquarie Harbour, which would soon become the site of one of the convict era’s most brutal places of punishment. Their work done there, the Mermaid was back in Sydney in late February, and in May she was off again.
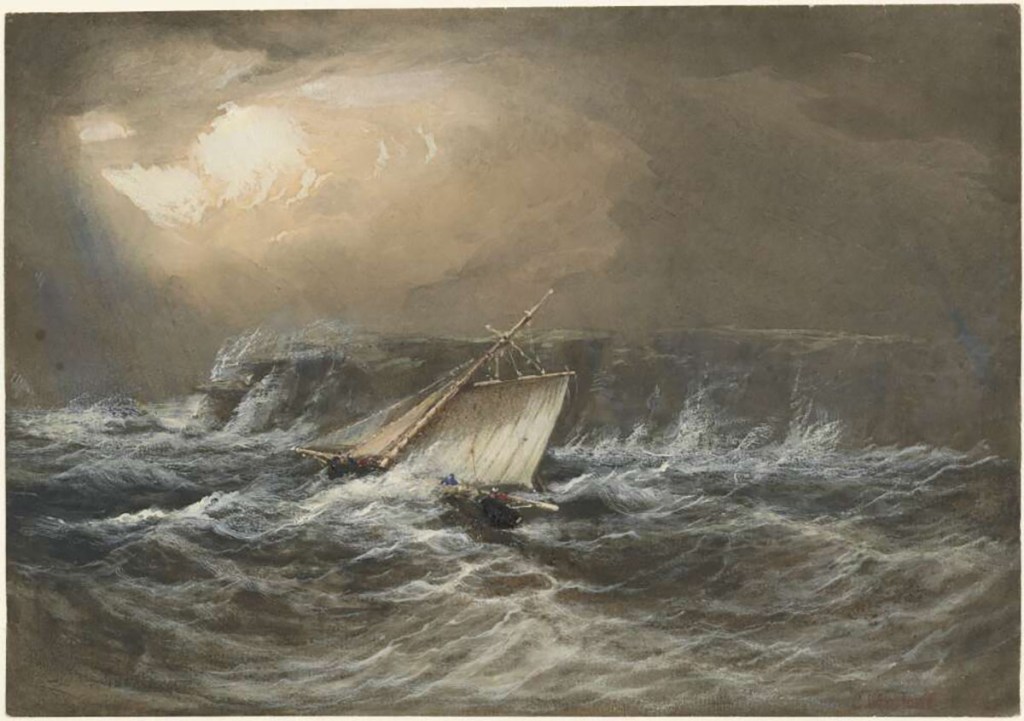
The third voyage, and King’s last in the Mermaid, saw them sail up the east coast of Australia on a circumnavigation of the continent. On 20 July, while sheltering in a bay he named Port Bowen at latitude 22.5 S (not to be confused with the present-day township of Bowen), the Mermaid ran aground and became stuck. It was only after considerable effort that the crew were able to warp the vessel into deep water, but she sustained serious hull damage in the process. The full extent of the injury would only become apparent months later.
The Mermaid continued north, passed through Torres Strait and King again started making a detailed survey of the north-west coast. However, the cutter had been taking on water ever since its beaching at Port Bowen. By September, she was leaking so badly that King was compelled to careen the vessel and attend to the leaking hull. With repairs completed as best they could, he then cut short his survey and ran down the west coast, across the Great Australian Bight, returning to Sydney in December. However, the Mermaid was very nearly wrecked within sight of her home port.
As they passed Jervis Bay, the wind was blowing strongly from the east-south-east and visibility was much reduced by heavy rain. Lt King steered a course that he thought would find them off Sydney Heads the following morning. But at 2 o’clock in the morning, King, thinking they were still 30 km from land, was surprised when a bolt of lightning revealed they were sailing directly towards Botany Bay’s south head. The Mermaid only just cleared that hazard but lodged on a rock off the north head before being lifted off by a large wave. She ploughed through breakers within metres of the rocky promontory with the sea surging and foaming around them. It was a very close call, but they were soon safely inside Sydney Harbour without further incident.
Lt King made his fourth and final survey in the Bathurst while the Mermaid underwent much-needed repairs. But that was not the end of the little cutter’s adventures. She was decommissioned from the Royal Navy and taken over by the NSW colonial government, where she continued to serve with distinction.

In 1828, the Mermaid received a major overhaul, including re-planking, new copper sheathing, and, most importantly, being re-rigged as a two-masted schooner. Then, in early 1829, she was tasked with helping dismantle the failed settlement at Raffles Bay on the Cobourg Peninsula. Once done there, they were to make for the remote settlement of King George Sound (present-day Albany) to deliver stores and dispatches. Under the command of Captain Nolbrow, the Mermaid departed Sydney on 16 May and headed north, keeping to the inner passage inside the Great Barrier Reef.
Tragedy struck at 6 o’clock in the morning on 13 June when, about 35 km south of present-day Cairns, the Mermaid ran grounded on a reef not recorded on King’s recently published naval chart. At 8 p.m., Captain Nolbrow and his crew, 13 men in all, took to the lifeboat with the hold bilged and water already over the cabin deck.
Twelve days later, as they continued north towards Torres Strait, the castaways were picked up by the Admiral Gifford. The Admiral Gifford was a 34-ton schooner on a speculative voyage through Australia’s northern waters and was ill-equipped to carry so many additional passengers. On 3 July, Nolbrow and his crew were transferred to the much larger Swiftsure, possibly in the vicinity of Pipon Island. Unfortunately, the Swiftsure was wrecked two days later near Cape Sidmouth and her crew, along with the Mermaid’s, were rescued by the Brig Resource.
Captain Nolbrow and his men eventually made it back to Sydney via the Swan River settlement (present-day Perth) in November 1829. The remains of the Mermaid were discovered on Flora Reef in 2009.

© Copyright C.J. Ison / Tales from the Quarterdeck, 2023.
To be notified of future blogs, please enter your email address below.