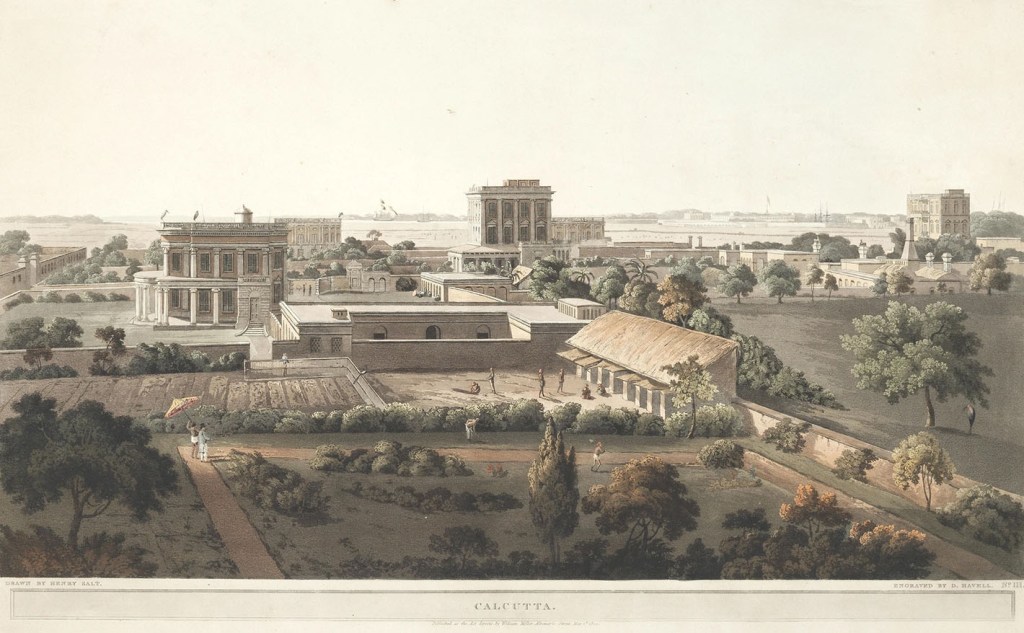
One of the first concerted efforts to escape from Sydney that did not involve trying to stow away on a homeward-bound ship took place in the latter part of 1790. Convicts, John Turwood, George Lee, George Connaway, John Watson, and John Strutton stole a boat and headed out to sea.
Turwood and his mates had endured unimaginable hardships since leaving England, for they had come out on the infamous Second Fleet. Unsanitary living conditions and malnutrition had taken their toll on the voyage out. One-quarter of the 1006 convicts who left England died before ever reaching New South Wales. Of those who were put ashore, nearly 500 were immediately hospitalised. Of those, 124 would soon be dead. By September 1790, Turwood and his mates had been in the penal settlement for just eight weeks, but they had no desire to remain any longer to see if their fortunes might improve.
Strutton had tried to escape once already. He had been smuggled aboard the Neptune and hidden among the firewood shortly before she was to sail back to England. However, sentries found his hiding place, and he was taken off the ship. He was flogged for trying to abscond, but the punishment only made him more determined to try again.

Soon after sunset on the night of 26 September, the five convicts stole a small flat-bottomed punt at Rose Hill and rowed down the Parramatta River into Sydney Harbour. Crammed in the small boat with them was one week’s supply of food, some cooking pots and other utensils, a few spare clothes and some bedding. At Watson’s Bay, just inside Sydney Heads, they put ashore and found another, much larger boat. Though it did not look particularly sturdy, it did have a mast and sail. Despite its shortcomings, the runaways thought they would have a better chance of surviving the open ocean in the larger boat. They transferred their belongings and headed out through Sydney Heads. By the time the bolters were reported missing and the two boats stolen, they were well on their way.
Turwood had told friends before he had set off that they were going to sail to Tahiti, a place elevated in his mind to a tropical paradise where they could live freely among the Islanders. Tales from sailors who had visited Tahiti and other Pacific Islands had returned to England with fanciful stories about their time spent there. However, just how he intended to accomplish the 6,000-kilometre voyage without a sextant, charts, a compass, or any other navigation aids is a mystery.
John Turwood was serving a life sentence for highway robbery. George Lee and George Connaway had stolen a pair of bullocks valued at £20. They had been sentenced to death, but that was later commuted to transportation for life. Watson and Strutton were each serving seven-year terms for stealing. Though nothing in their convict records suggests any of them had a nautical background, at least one of them knew how to handle a small vessel under sail.
After leaving Sydney Harbour, they set a course north, always remaining close to the coastline. When the sheltered waters of Port Stephens beckoned, they pulled in, and that’s where they stayed. After sailing 150 km, that was as close as they got to Tahiti. The local Aboriginal people, the Worimi, made them welcome and adopted them into their community. Over time, Turwood and the others learned to speak their language and were given Worimi names. They also seem to have undertaken formal initiation rituals, and at least a couple of the men took wives and began raising their own families. However, life was a constant struggle for the men, who were unaccustomed to the diet and customs of the Worimi people, especially in the beginning. Strutton died, although the circumstances and date of death were never recorded. Nonetheless, the other four lived there for five years and would have remained longer had a British warship not shown up.
HMS Providence pulled into Port Stephens in mid-August 1795. She had just crossed the Pacific Ocean but had been unable to enter the Heads because of a strong westerly wind blowing off the land. Captain Broughton thought he would wait a few days in these sheltered waters before trying again. While there, he discovered Turwood and the other three white men living with the Aborigines. Broughton described them in his log as “miserable, half-starved objects, depending on the hospitality of the natives for their subsistence …” He offered to return them to Sydney, assuring them that they would likely not face punishment. Lee, Connaway and Watson immediately accepted the offer; however, Turwood was initially reluctant, but Broughton was eventually able to convince him to return as well. The arrival back in Sydney after a five-year absence was met with considerable surprise and of the runaway convicts in Sydney caused some consternation among the authorities, for they had long been given up for dead. But, true to Broughton’s word, they appear to have escaped punishment. Perhaps the Governor thought five years in the wilderness had been punishment enough.

John Turwood and George Lee would flee from Sydney again in September 1797. They joined 13 other runaways who seized the small colonial cutter Cumberland near the mouth of the Hawkesbury River. After putting the captain and crew ashore, they headed out to sea. Neither the Cumberland nor the runaway convicts were ever seen again.

© Copyright C.J. Ison / Tales from the Quarterdeck, 2025.
Please enter your email address below to be notified of future blogs.



