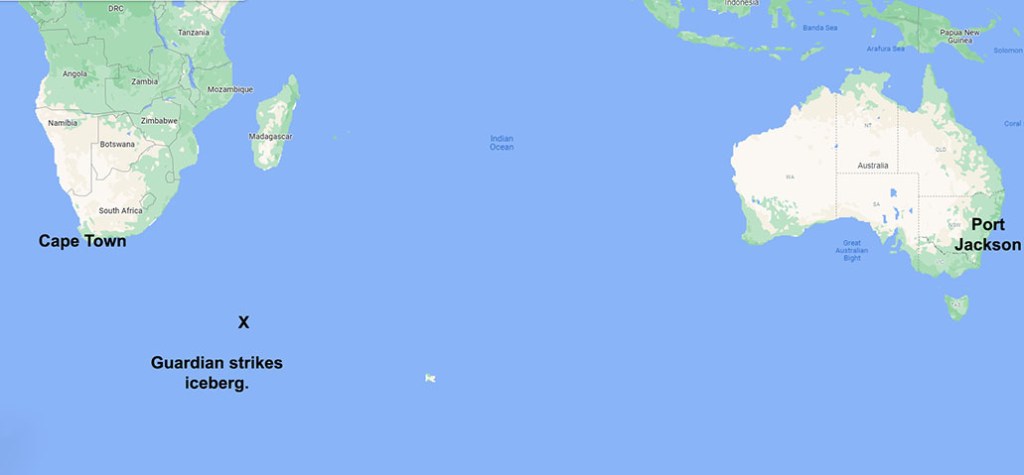
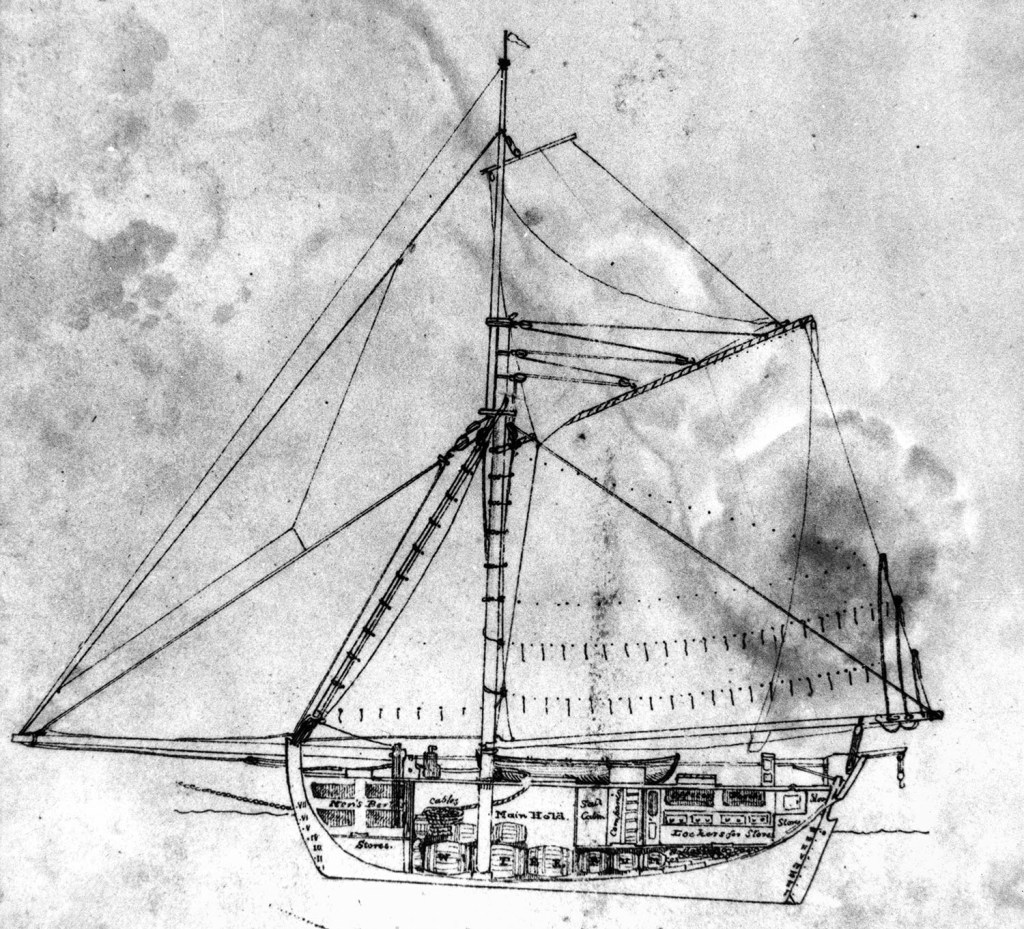
On a hot December night in 1831, a storm rolled across Moreton Bay as they often do at that time of year. Outside the Amity Point pilot house, nearly a dozen convicts huddled under a sheet of canvas as they bided their time. There was a small schooner anchored a short distance offshore, and the storm would provide the soaking prisoners with a rare opportunity to escape.
But what the hapless runaways did not know as they seized the Caledonia and sailed her out of Moreton Bay, their self-appointed leader was a dangerous psychopath, and they would be swapping one reign of terror for another far worse. Three of them would soon be murdered. A fourth would be abandoned on an inhospitable island, and the rest would flee for their lives at the earliest opportunity.
The Caledonia had pulled into Moreton Bay the previous day to collect a whaleboat, which belonged to the sailing ship America. The crew had used it to reach Moreton Bay after their ship was wrecked further north. Two Sydney businessmen had purchased the salvage rights to the wrecked ship and sent Captain George Browning north to retrieve the boat and strip the America of everything of value. Browning had reported to the Amity Point pilot station and explained their unexpected visit. He was now waiting for the boat to be brought down the Brisbane River before he continued on his way to the wreck site.

That night, as lightning streaked across the sky and deafening claps of thunder boomed around them, the convicts got to work. The guard had taken shelter and the raging storm muffled any noise they made. They easily dug down through the sand and tunnelled under the pilothouse wall. A couple of them crawled inside, stole the keys to the boat shed and armed themselves with muskets and pistols while the pilot and a guard slept. Then they jumped into the pilot boat and rowed out to the Caledonia. No guard had been posted on deck, and the crew were easily overwhelmed before they had fully awoken. The Caledonia’s crew were ordered into the pilot boat to make their way back to Amity Point using only one oar. However, the convicts held on to Captain Browning. He was needed to navigate the schooner to the tiny island of Rotuma, 3000 km away. By dawn, the Caledonia was heading out to sea, as the crew drifted back to shore to raise the alarm.
The leader of the runaways was a former sailor named William Evans. He was unusual, for he had come to New South Wales as part of the crew of a merchant ship. One night while moored in Sydney Harbour, Evans had broken into the captain’s cabin and stolen a purse full of money. He was spotted leaving the ship in a small dinghy and was soon caught. Evans was found guilty and sentenced to seven years’ hard labour at Moreton Bay. Now, in the closing days of 1831, Evans still had three more years of back-breaking toil, poor rations and loathsome living conditions to endure. When he realised there was a chance he could make his escape on the schooner, he pounced, convincing the rest of the prisoners to join him.
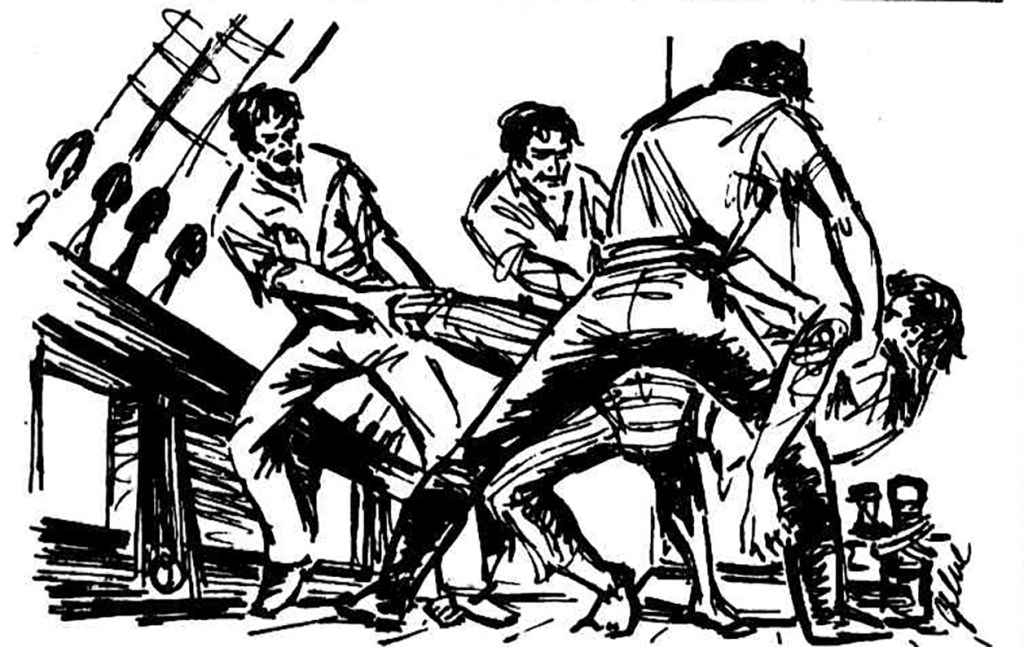

After they had been at sea for a week, tensions came to a head among the convicts. The common purpose that had seen them work together to seize the ship and escape had been replaced by bitterness and division. After hearing a rumour that a mutiny was looming, Evans struck first. He stood outside the entrance to the crew’s cabin, backed up by two mates, and ordered one of the mutineers to come on deck. As he emerged, Evans shot him point-blank in the head. Evans then ordered two others to come out, and they were killed on the spot. That ended any thought of challenging his leadership.
About a week later, the schoonerstopped at New Caledonia for water. Evans’ right-hand man, Hugh Hastings, and a couple of others took a boat out to fill the water barrels. But, while they were gone, a party of Islanders came out to the schooner, indicating that they wanted to trade. As the Islanders outnumbered those on the schooner, they were barred from boarding. Only a volley of shots fired over their heads saw them leave. Fearing they might return under the cover of darkness, Evans had the Caledonia taken out to sea. But, when Hastings returned to find the schooner missing, he thought the worst and swore he would kill Evans for his treachery.
Hastings and the others spent an uncomfortable night in the boat, but in the morning the Caledonia returned to pick them up. When Evans heard that Hastings had threatened him, he gave his mate two choices. Either stay on the island and take his chances with the hostile natives, or be shot. Hastings remained on the island when the Caledonia sailed away.

The Caledonia continued back out to sea and headed for the tiny island of Rotuma, still 1000 km away. Evans had heard rumours that whaling ships regularly stopped there for water and fresh supplies. He planned to join the next American whaler to visit Rotuma and work his way to the United States.
The Caledonia dropped anchor off Rotuma a week or so later, however, their stay was cut short. One of the convicts bragged that they had just escaped from Moreton Bay. When Evans found out, he was furious and vowed to kill the man, but he fled into the bush before the threat could be carried out. Evans felt it was no longer safe to stay on Rotuma, so he ordered Captain Browning to set sail.
The Caledonia eventually pulled up off Savai’i Island in Samoa. As soon as they dropped anchor, three more of the convicts jumped ship and fled inland, taking with them three women Evans had kidnapped off Rotuma. Of the ten convicts who escaped with Evans, only three were left.
Evans went ashore and learned that whaling ships regularly called in there for supplies, so he scuttled the Caledonia and awaited the next ship. Browning, whose life had hung in the balance since leaving Moreton Bay, was finally able to escape Evans’s clutches. A local chief had taken a liking to Browning and gave him protection as Evans and his mates kept their distance. When, a fortnight later, the whaler Oldham dropped anchor, Browning raced out to meet the captain. Browning told him that Evans was an escaped convict and had murdered three men since fleeing Moreton Bay. The Oldham’s captain and crew went ashore and brought Evans back to their ship in chains. Evans’ mates, by then, had taken off into the bush. However, Evans would never front court for his crimes. On the way back to Sydney, he jumped over the side of the ship, preferring to drown rather than face the hangman.
Several months after the Caledonia sailed out of Moreton Bay, Captain Browning arrived back in Sydney, long after he had been given up for dead.
The full story is told in A Treacherous Coast: Ten Tales of Shipwreck and Survival from Queensland Waters available through Amazon.

© Copyright C.J. Ison / Tales from the Quarterdeck, 2022.
To be notified of future blog posts, please enter your email address below.